Gingivitis – Causes, Symptoms and Prevention
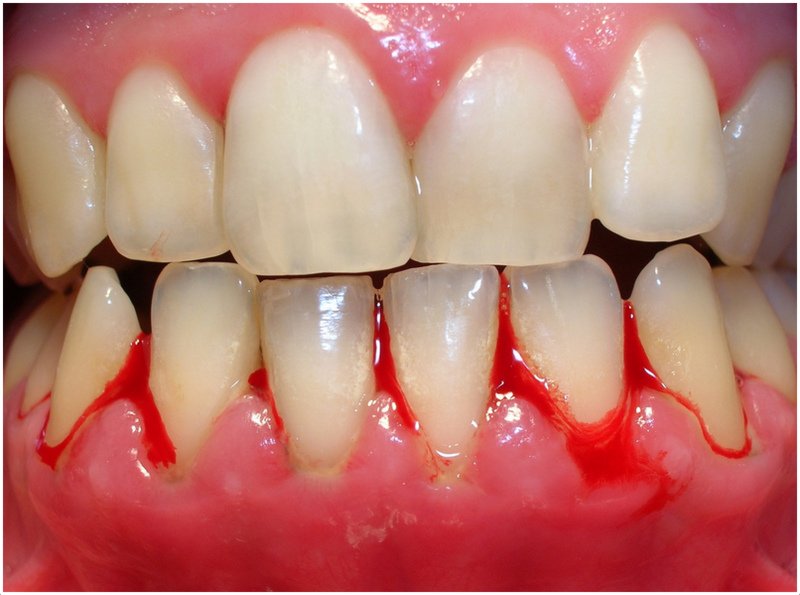 It is an inflammation of the gums, usually caused by a bacterial infection. If not treated properly, it might lead to more serious infection and eventually to tooth loss. Gingivitis (gum inflammation) usually precedes periodontitis (gum disease). However, it’s not always that all gum inflammations progress to periodontitis.
It is an inflammation of the gums, usually caused by a bacterial infection. If not treated properly, it might lead to more serious infection and eventually to tooth loss. Gingivitis (gum inflammation) usually precedes periodontitis (gum disease). However, it’s not always that all gum inflammations progress to periodontitis.
How does Gingivitis happen?
Food can get trapped in the space between the gums and the teeth and cause a gum infection. Plaque a thin film of bacteria constantly forms on the surface of your teeth. As plaque advances, it hardens and becomes tartar. If plaque extends below the gum line, an infection develops.
If gingivitis is left unchecked, the infection may cause the gums to separate from the teeth. This impacts the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth. As a result, the tooth may become loose.
Causes for gingivitis
The following are common factors:
- Smoking or chewing tobacco
- Diseases like Diabetes, HIV etc
- Substance abuse
- Using oral contraceptives
- Misaligned teeth
- Poorly fit dental appliances
- Broken fillings
- Hormonal changes due to Pregnancy
- Genetic factors
Symptoms
Many people aren’t aware that they have gingivitis. It’s possible to have gum disease without any symptoms. However, the following can be symptoms:
- Red, tender, or swollen gums
- Bleeding of gums when you brush or floss your teeth
- Gums that have pulled away from the teeth
- Loose teeth or pus between teeth and gums
- A change in how your teeth fit together when you bite (malocclusion)
- Pain when chewing
- Sensitive teeth
- Partial dentures that no longer fit
- Foul-smelling breath that does not go away after you brush your teeth
Prevention
If proper plaque control is practiced gingivitis can be prevented. That includes deep cleanings at least twice a year by your dentist and daily brushing and flossing. Brushing prevents plaque to deposit while flossing removes food particles and plaque from in between the teeth and under the gum line. Antibacterial mouth washes can reduce bacteria that cause plaque and gum disease.
Other health and lifestyle changes that will decrease the risk, severity, and speed of gum disease development include:
- Stop smoking or chewing or Tobacco.
- Reduce stress.
- Maintain a well-balanced diet to help your immune system fight infection.
- Avoid clenching and grinding your teeth.
During your regular check-ups, get advice on health of your gums as well. If you are susceptible to gum infection or disease , your dentist would suggest you treatments or refer you to a periodontist.
