About Trench Mouth
Medically known as Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis or ANUG or Trench mouth ; is a common, non-contagious infection of the gums with sudden onset. The main features are painful, bleeding gums, and ulceration of the sections of gum between adjacent teeth. It is also known as Vincent’s stomatitis and Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
The term ‘trench mouth’ comes from World War I, when many soldiers in the trenches developed the infection. This disease is now rare, but minor gum infections involving just a few teeth probably occur relatively commonly. The severe form usually affects only people with an impaired immune system. It is most common in teenagers and younger adults and is found mainly in underdeveloped nations and areas with poor nutrition and living conditions.
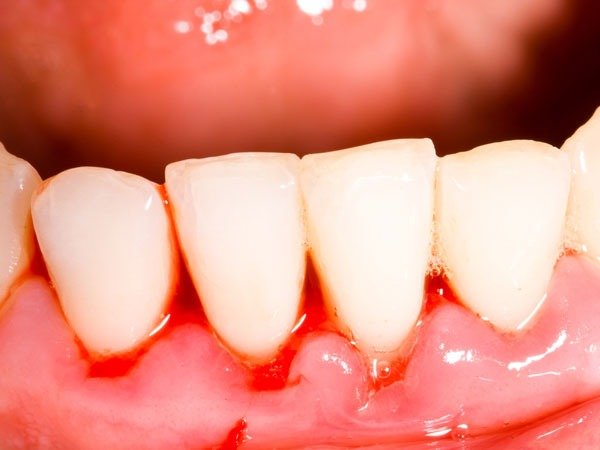
This gum infection is caused by a buildup of harmful bacteria in the mouth due to poor oral hygiene, however. Red, sensitive, and bleeding gums are symptoms of a condition known as gingivitis. This gum disease is a rapidly progressing form of gingivitis.
Causes:
Trench Mouth is caused by an infection of the gums due to the excess growth of harmful bacteria. Gingivitis patients, are at a higher risk of developing this advanced infection. If left untreated, the infection further damages gum tissue leading ulcers and possible tooth loss. The main causes are as follows:
- Poor dental hygiene
- Poor nutrition
- Smoking
- Stress
- A weakened immune system
- Infection of the mouth, teeth, or throat
- HIV/AIDS
- Diabetes
Symptoms:
Its symptoms are similar to that of Gingivitis but Trench Mouth progress much more rapidly as compared to Gingivitis. Below are the signs to keep in mind to get timely treatment.
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums
- Pain in the gums
- Bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
- Bleeding while brushing
- Ulcers (crater-like) in the mouth
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Grayish film on the gums
While the condition rarely has serious side effects, ignoring symptoms can lead to potentially serious complications, such as: tooth loss, destruction of gum tissue, trouble swallowing, oral diseases that can damage bone and gum tissue coupled with severe pain
Treatment and Management:
This gum disease is treatable and can be managed if proper precaution and care is taken. This includes:
- Antibiotics to stop the infection from spreading further.
- Pain relievers such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen.
- Professional cleaning from a dental hygienist.
- Regular oral hygiene and cleaning like brushing and flossing your teeth thoroughly twice a day.
- Warm salt water rinses and rinsing with hydrogen peroxide can ease the pain of inflamed gums and also help remove dead tissue.
- Avoid tobacco products.
- Eat a healthy diet and avoid hot and spicy foods till your gums heal.
- Keep stress level down.